Interest rate
Interest rate may comprises of 3 components
- Risk free real rate i.e. compensation for sacrifice current consumption
- Inflation premium i.e. compensation for the loss of purchasing power
- Risk premium i.e. compensation for bearing risk
Based on the these components, there are 4 types of interest rates:
- Risk free real rate of return
- Risk free nominal rate of return
- Risk adjusted real rate of return
- Risk adjusted nominal rate of return
Sum: Consider a project with the following cash flows:-
Year 0 1 2 3
Cash Flow( in lacs) -500 200 250 200
These cash flow include inflation of 3% p.a
Cost of capital 12%. Find NPV of the project
DCF
As per discounted cash flow techniques (DCF). The intrinsic value of an asset, is the present value of the future cash flow discounted at the required rate of return
There should be consistency between the nature of cash flow and discount rate
- Nominal/real cash flow should be discounted at Nominal/real rate
- Certain/uncertain cash flow should be discounted at risk free/risk adjusted rate
Different type of yield
Bond equivalent yield (BEY): Since most bonds pay coupon semi annually there is a tendency in the market to compute BEY which is actual a special case of MMY with a base period of 6 months
Sum: An investor purchase a stock at Rs600. He sold the same at the end of 2 months for Rs625 and received a dividend of Rs 5, Find a) HPY , b) MMY C) EAY & D) BEY
Implied interest rate
Given a cash flow stream, the implied interest rate the one which equates outflow with the inflow standing at a particular time.
From a computational purpose:
- If the CF span over at most 2 periods, we are suppose to exactly solve for the interest rate using linear or quadratic equation
- If the CF span over more than 2 periods, we compute the interest rate approximately by the process of trial & error & the technique of linear interpolation or extrapolation
Sum: Consider a project with the following cash flows:-
Year 0 1 2 3
Cash Flow( in lacs) -500 200 250 200
Calculate IRR
Bond Valuation
The intrinsic value of a bond is the PV of the future coupon & redemption amount discounted at the required rate of return. If the market price is lower/higher than intrinsic values, then bond is underpriced/overpriced & should therefore be purchased/short sold respectively
Sum: Consider a two year Rs1000 face value 10% coupon rate bond which pays coupon semiannually. Find out the intrinsic value of the bond if the required rate of return is 14% p.a. compounded semiannually. Should the bond be purchased at the current price of Rs 965.
Annuity
An annuity is a series of equal periodical payments. If the payments are made at the end /beginning of each period, we call is an ordinary annuity/annuity due respectively
Sum:. X ltd is taking a machine on a 5 yrs lease. It has 2 options
Option1: Lease rentals Rs 10L payable at the end of each year
Option 2: Lease rentals Rs 9.5L payable at the beginning of each year
If the discount rate is 14%, find out the option the X ltd should choose.
Perpetuity
A perpetuity is annuity to continue for ever
If there is a cash flow stream which is expected to grow at a constant growth rate for ever its PV is given by
Equity valuation
As per the dividend discount model (DDM), intrinsic value of a share i.e. the PV of expected future dividend discounted at the required rate of return
There are three patterns if dividend forecast
1) No growth DDM: This will be applicable for the firm having 100% payout ratio such DPS=EPS=perpetuity
2) Constant growth DDM: In this case, the firms dividend is expected to grow at a constant growth rate forever.
3) Multiple growth DDM: The firm will exhibit supernormal growth say for the first ‘n’ yrs beyond there would be perpetual normal growth rate.
Sum 1
X LTD has 100% payout ratio and is a no growth firm. It has an EPS of Rs 15 for the year just ended and the stock is presently trading at Rs. 132. If ROR is 14% p.a. Find out the intrinsic value of the share and comment on its current price.
Sum 2
A firm recently paid a dividend of Rs 8 per share. This is expected to grow 6 p.a. for ever. Find out the value of the share if RoR is 14% p.a.
Sum 3
X ltd reported an EPS of Rs12 for the year just ended and a payout ratio of 40%. The earnings are expected to grow at 30% p.a. for the next 4 years. Beyond the 4th year, growth rate would be 6% forever. Find out the intrinsic value of the share if ROR is 18% p.a
Continuous compounding
Stock and bond prices changes on a real time basis given rise to the concept of continuous compounding. Obviously, if interest rate is ‘I p.a.’ compounded continuously, the interest factor i.e future value Rs 1 is more than (1+i)
Specifically the interest factor becomes ei
Sum: Consider a stock trading at Rs750. This stock has announced a dividend of Rs 25 payable 6 mts from now. If interest rate is 9% p.a. compounded continuously, find out the ex-dividend stock price. ( given e0.0225=1.0227)
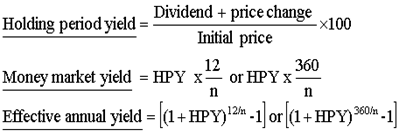

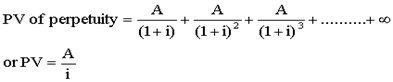
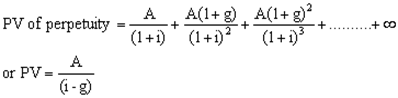
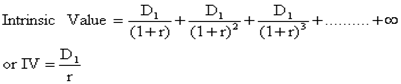
No comments:
Post a Comment