Foreign Exchange Market
It is an over the counter market where currencies are bought and sold against one another. RBI regulates the markets and appointed banks who act as authorized dealers. Banks acts as market makers and provide bid- ask rates.
Purchase and sale of foreign currency
Nostro Account:
Vostro Account:
Retail Market
The forex market can be divided into three tiers
1. transaction between RBI and authorized dealers
2. Inter-bank or wholesale market.
3. Retain market.
The rate applicable in the retail market are known as telegraphic transfers or TT rates. These rates are arrived by charging TT commission to the inter-bank rate.
Exchange rate quotation
Direct quote:
Indirect quote:
American quote vs merchant quote :
Inter-bank quote vs merchant quote :
Inverse quote :
Cross Rates :
Bid Ask Spread
Depends upon:
- Turnover of the currency. Higher the turnover, lower the bid-ask spread & vice versa
- Competition between the market makers. Higher the competition exists, lower the spread & vice versa
Spot and forward rates
Spot rates is a rate applicable for a spot transition i.e. delivery 2 business days ahead. Forward rate is the rate applicable in a forward contract i.e. a contract to buy or to sell foreign currency at a some future date at a rate agreed upon today. Both spot and forward rates are determined by demand and supply forces. Thus forward rates can be higher/lower then spot rate and accordingly the currency is said to at a forward premium or discount
Annulated forward premium or discount
Annualised forward premium on currency B: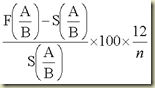
A negative discount will imply a discount
Swap Points
Swap points refers to difference between the spot and forward rate. The swap points are low/ high, they are added to the spot rate. Similarly the swap points are high/ low, they are deducted from the spot rates.
Exchange margin
Exchange margin is the extra amount or percentage by the bank over and above the rate quoted by the bank it represents commission, transaction related expenses etc
Arbitrage
Arbitrage refers to simultaneously buying and selling identical/Similar assets with a view to make risk-less profit. Two way arbitrage in a currency market involves buying one currency from a bank and selling it to another bank to make a profit.
- Geographical arbitrage:
- Two way arbitrage
- Inverse rates and two way arbitrage
- Three way arbitrage
- Cross Rates
- Covered interest arbitrage
Followings are the spot exchange rates quoted at three different forex markets :
USD/INR 48.30 in Mumbai
GBP/INR 77.52 in London
GBP/USD 1.6231 in New York
The arbitrageur has USD1,00,00,000. Assuming that there are no transaction costs, explain whether there is any arbitrage gain possible from the quoted spot exchange rates. (Nov. 2008)
2 comments:
Thank you very much for your kind words.
NSE ACCOUNT
tradeeasy is the trading platform for dealing in securities at lowest brokerage and instant online client support and offers highest leverage.
Post a Comment