Types of option
| Long (+) | Put (-) |
| Enjoys the rights | Suffers on obligation |
| Pays initial premium | Receive initial premium |
| Pays of will be positive or zero | Pays of may be negative or zero |
| Suffer time decay | Enjoys time decay |
| Long on volatility i.e. gains if volatility rises | Short on volatility i.e. gains if volatility |
Based on maturity
| American | European |
| Can be exercised on or prior to maturity. Eg stock option in India | Can be exercised only on maturity. Eg Index option in India |
Based on right
| Call | Put |
| Right to buy | Right to sell |
| Bullish | bearish |
| Pay off : Max (s-E/0) | Pay off : Max (E-S/0) |
| 1.Intrinsic value = Max (S-E,0) | 1.Intrinsic value = Max (E-s,0) |
Moneyless of an option
| Option | S<E | S=E | S>E |
| Call | Out of the money | At the money | In the money |
| Put | In the money | At the money | Out of the money |
| Intrinsic value | Time value |
| F(S,E) | F(t,δ,r), f (time,volatility, risk free rate of int) |
| C+ is a substitute of S+, Since C results in saving interest, call is a positive function of interest rate. | Time: higher the time left to maturity, more valuable is the option |
| P is substitute of S-,since P+ results in loss of interest . Put is a negative function of interest rate | Volatility: If volatility causes the option to be exercised , higher volatility benefits the option buyer , however if volatility causes the option to lapse, pay off is zero, higher the volatility higher the option value |
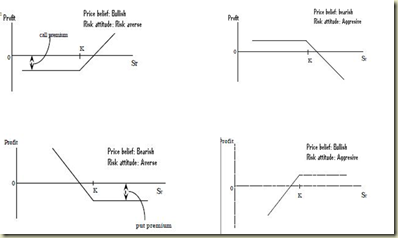
Pay off profile & profit diagram of an option
Hedging through options
Hedging foreign currency payable (C+,P- relationship)
Alt I: Buy calls (C+)
Alt II: Sell a put (P-)
Alt III: Buy calls (C+), Sell a put (P-) at the same E
Alt IV: P- at a lower E(E1) & C+ at a higher E(E2) such that net premium is NIL.
Hedging foreign currency receivable (P+,C- relationship)
Alt I: Buy Put (P+)
Alt II: Sell a call (C-)
Alt III: Buy puts (P+), Sell a call (C-) at the same E
Alt IV: Range forwards (P+ at E(E1) & C+- at a E(E2) [E1<E2]
Speculation using options
A) Synthetic strategies
Strategy I: Protective put ( P+;S+)
This involves buying a stock & hedging the downside by buying a put. Its profit profile would be similar to long call (C+)
Therefore P+, S+=C+
Strategy II: Covered call writing ( P+;S+)
This involves buying a stock (S+) & for going the upside of the stock by writing a call (C-) which in turn reduces the effective cost of holding the share.
We will find that this strategy is equivalent to put writing i.e. S+;C-= P-
B) Combination strategies
C) Spread strategies
i.Time/calendar horizontal spread: Same strike price but different maturity
ii.Price/vertical spread: Same maturity but different strike price
- Butterfly spread: based on volatile/non-volatile price belief, It will involve 3 strike price ( C+,2C-,C+)
- Bull & bear spread : It will involve two strike price
iii.Diagonal spread: Different maturity and different ‘E’
Valuation of option
The value of an option i.e. option premium comprises of
A. intrinsic value
B. Time value
This functional relationship need to be opened out in the form of option pricing model
A Binomial model
B. Black scholes
Before we evaluate this model let us cover put- call parity.
Put- call parity
It is a relationship between European put and call option on the same stock for the same maturity at the same E. It is given by
Po + So = Co + PV of E
This parity is based on prevention of arbitrage principle. If two portfolios have identical pay off the cost of portfolios should be same to prevent arbitrage.
BINOMIAL MODEL
Option pricing requires the specifications of the stock price behavior. The binomial model is based on a simple assumption that if stock price today is S it can take up only two value uS and dS on maturity .
The pricing of options via binomial model can be done by two methods
Method 1- Risk free portfolio approach
Method 2- Risk neutralization Approach.
Black scholes model (BSM)
BSM is a limiting case of binomial model. As the nos of steps om the nomp,oa; ,psde; tends to infinity the binomial model tends to BSM
BSM is an elegant model & elegancy has been obviously achieved by taking a no. of assumptions
1.Markets are efficient ( i.e. no transaction cost , no taxes, no restrictions on short selling & perfectly divisible securities)
2.Options are only European
3.Option are on non-dividend paying stocks
4.Risk free continuously compounded interest rate (ir) is known & constant
5.The Annualised volatility of stock return is know as constant
6.Stock price are log normally distributed
Option Greeks
We know that option price = f(S,E,r,t,δ)
Thus option pricing continuously change in the mkt on account of change in these factors. The sensitivity of option price with each factor, taking others constant is know as option Greeks.
Delta
It is sensitivity of option premium to stock price
Delta of a call is potive & that of put is negative. Thus if delta of call is 0.4, it means that if share price goes up by re1, call predecessor relation is expected to rise by 0.4
Theta
It is the rate at which time decay occur, at par
Theta is negative for both call & put. Thus if theta of call is -4, it means that with the passage of a day call premium is expected to fall by Rs4/-
Vega
It is sensitivity of option premium to volatility at par
Vega is positive of equal for both call & put. Thus if Vega of an option is 7, it means that if volatility goes up by 1%, option prem is expected to rise by Rs7.
RHO
It is sensitivity of position premium with int. rate, at par
Rho of a call is positive & that of a put is negative. Thus if rho of a call is 0.7, it means that if int. rate goes up by 1%, call prem is exp to rise by Rs 0.7.
Gamma
It is the rate of change of delta wrt stock price, at pat
Gamma is positive & equal for both call & put. Thus if gamma of a option is 0.03 it means that if share price goes up by Re1, delta of the option is expected to rise by Rs0.03.
No comments:
Post a Comment